What is a sugar addiction?
It is well known that, like cigarettes or drugs, sugar can also be addictive. An above-average consumption of sweets/sugar has a negative effect on body weight and health, which can lead to sugar addiction.
We talk about sugar addiction when a constant desire for sweets is created.
The reward system in the brain and releases dopamine. This has been shown to be activated by foods high in sugar and is similar to some medications.
How sugar addiction threatens your health
Sugar addiction can affect anyone and many are unaware of their addiction. Normal for many is the daily consumption of sugar, desserts, cakes, sweets, sweet bites and sweetened drinks. But they already feel how sugar consumption makes many people ill.
Sugar is also a drug
Of course, sugar is not officially a drug. Sugar would then no longer be allowed to be added to our food and would not be sold to children. In addition, there would then have to be warnings on products, such as sugar is quickly addictive.

Sugar addiction creates a constant desire for sweets

Sugar addiction - pay attention to nutritional values and reduce sugar consumption
The development of sugar addiction
The main nutrients in our diet are fat and carbohydrates as well as protein. Depending on the composition of sugar and starch, carbohydrates have a different influence on our blood sugar level.
Carbohydrates are divided into single, double and multiple sugars. The number of sugar chains is decisive here.
Glucose (dextrose) is a single sugar.
The common household sugar (sucrose) consists of two molecules, fructose and glucose. That is why it is counted among the dual sugars.
Multiple sugars contain three to nine molecules. An example of multiple sugars are oligosaccharides, which are an essential component of rice syrup.
If a sugar contains more than ten single sugar molecules, it is called a polysaccharide. These include, for example, starch, dietary fibre and dextrins.
Continuous sugar intake disrupts the interaction of neurotransmitters and brain metabolism
The blood sugar level rises as the length of the sugar chain decreases.
The blood sugar level rises as the length of the sugar chain decreases.
Our pancreas secretes the hormone insulin as soon as we consume carbohydrates. Without the hormone, sugar would not be able to pass from the blood into the cells and no energy (ATP) could be produced.
Blood sugar rises within ten to twenty minutes of eating a bar of chocolate. At the same speed, the pancreas releases a lot of insulin. Afterwards, the blood sugar level drops again very quickly.
The brain reacts very sensitively to this sharp drop in sugar and a piercing feeling of hunger sets in. Other foods with a high glycaemic index, such as pasta and pastries, also trigger a rapid rise in blood sugar.
It is the brain that is addicted, because it shuts down free will due to an "energy crisis". You eat the whole bag of gummy bears, a bar of chocolate and maybe even that second plate of pasta. But what is the reason for this?
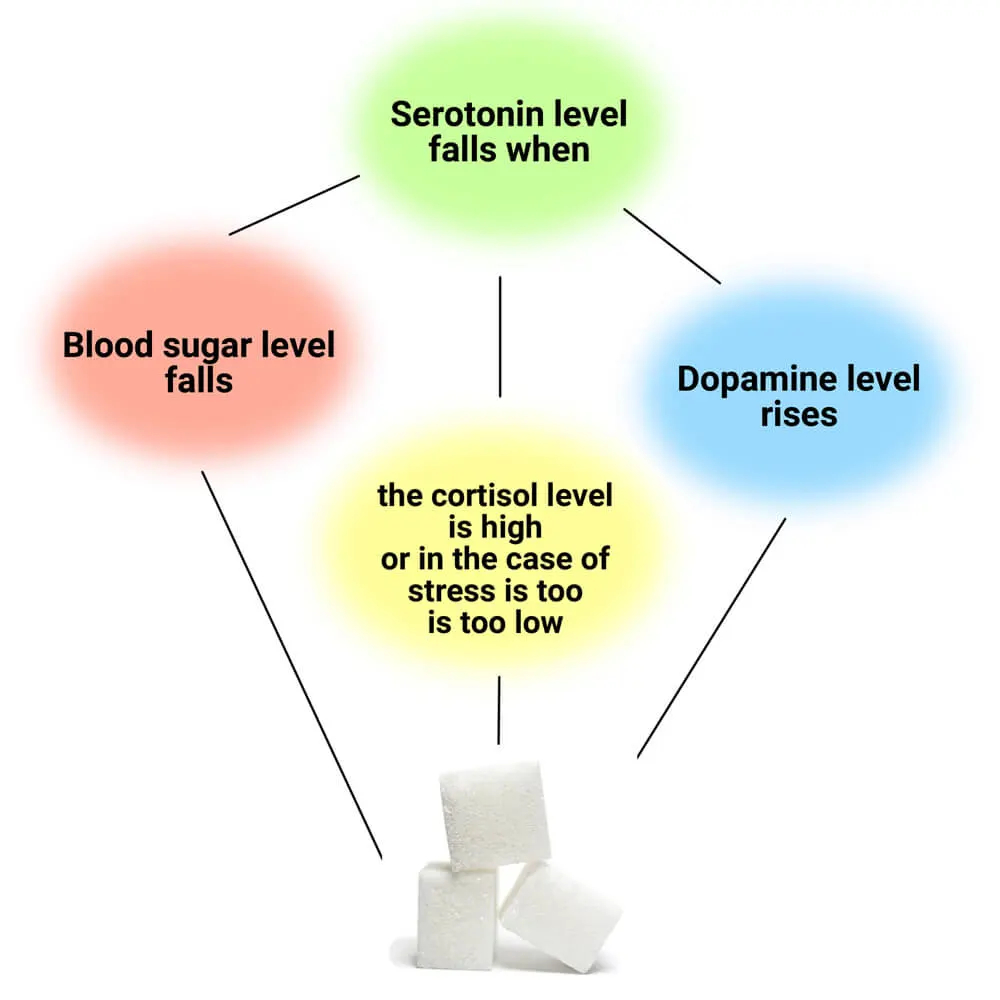
The disturbed interaction of dopamine, cortisol and serotonin.
It is the disturbed balance between the various neurotransmitters in the brain that causes addiction. In sugar addiction in particular, the messenger substances are serotonin and dopamine.
The serotonin level falls and rises analogously to the blood sugar level. Since the hormone serotonin ensures a good mood, low serotonin levels make us feel unhappy, irritable and listless. The likelihood of developing an addiction increases the lower the serotonin level.
Dopamine is both a hormone and a neurotransmitter in the nervous system. The higher the blood sugar rises, the higher the dopamine level rises.
Its property is essential in the context of sugar as a rewarding feel-good substance. A feeling of well-being is evoked when a chocolate bar is eaten. The desire to experience this feeling again quickly arises.
After some time, however, the body gets used to the amount. In order to achieve a similar feeling level as before, the body has to take in more and more sugar. A vicious circle begins.
As the dopamine level increases, the serotonin level decreases.
In stressful situations, the stress hormone cortisol, which regulates the blood sugar level, is increasingly released. It does this by ensuring that there is always enough glucose available from the body's reserves. The increased levels of insulin and cortisol briefly keep you focused on one task at a time.
Due to the increase in dopamine, the mood is also good. However, if one is under constant stress, the low serotonin level takes effect.
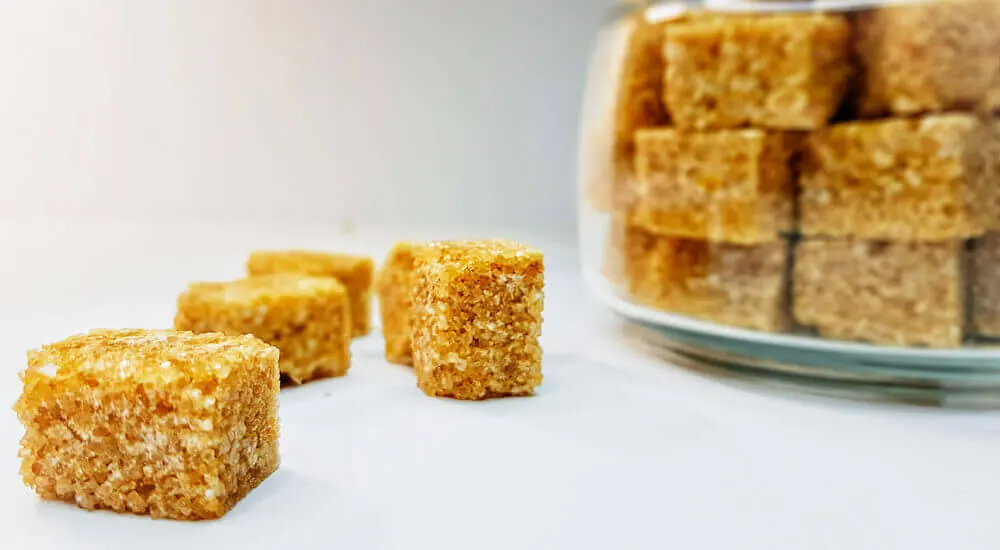
On average, each person consumes about 47 sugar cubes per day. This means nutritional stress for every single cell of the body. To counteract the increased cortisol level, people often reach for sweeteners.
At first it often helps, but in the long run the cortisol level drops below normal. This results in a feeling of indisposition, which tempts you to reach for sweets again.

Foods with high sugar content have been shown to activate the so-called reward system

Defeat sugar addiction

Do you suffer from sugar addiction?
One speaks of an addiction as soon as one is dependent on a certain substance and can no longer do without it. These are indications of a sugar addiction:
- Frequent snacking, in between or secretly
- Stockpiling sweets for the weekend
- Lack of ability to ration sweets and feelings of guilt as a result
- Love of sweet drinks and junk/fast food, despite subsequent sluggishness
- Periods of sugar-free eating following cravings
- Sweets as a release from stress
- Tension, nervousness and restlessness after a meal


How carbohydrates with different glycaemic indexes work.
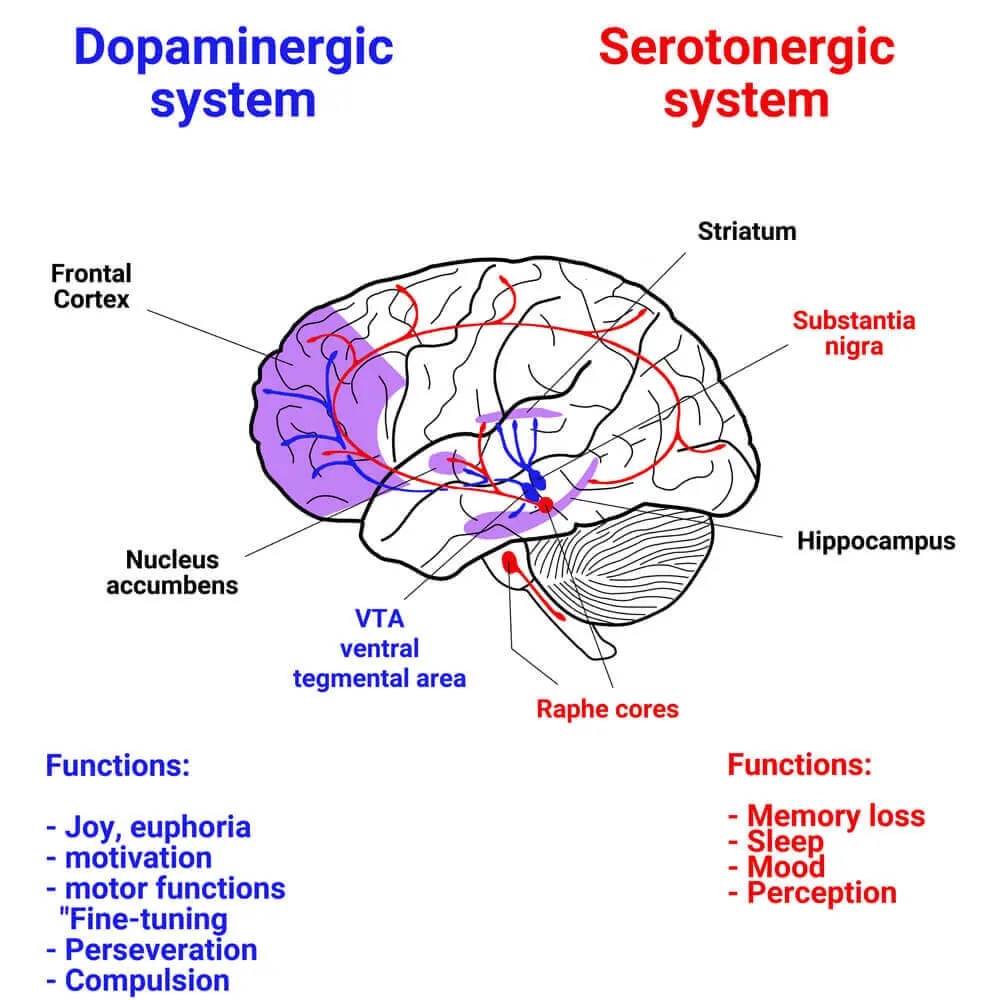
Serotonin and dopamine representation in the brain


Per capita consumption of sugar
The average annual sugar consumption per person in Germany is about 35 to 40 kilograms. In the USA and Switzerland, this figure is almost twice as high.
The sugar consumed is not just about the quantities used for coffee or cake batter. It also counts the sugar contained in jam, cocoa drinks, nut nougat cream, juices, soft drinks, crisps, biscuits or muesli, for example. This type of food does not show the amount of sugar.
The relief for their teeth when even a part of the sugar consumed daily is saved becomes clear. Besides the caries-inhibiting effect of Stevia, the sweetener is also said to prevent the formation of plaque (dental plaque).

Reduce sugar consumption!
Summary: The craving for sweets arises because:
- One is plagued by dissatisfaction (serotonin)
- The brain's reward system has learned to do so (dopamine)
- You suffer from stress (cortisol)
- The blood sugar level is extremely low
The interaction of neurotransmitters and brain metabolism is disturbed due to continuous sugar bombardment.

Sugar addiction - what you should know about sugar
How does sugar addiction threaten health?
The mitochondria in the cells overheat with a permanent supply of sugar. Mitochondria are referred to as the "batteries of the cell" because they provide the cell with energy in the form of ATP. The cells react to the excess sugar by becoming immune to insulin.
This leads to the sugar remaining in the blood. In addition, insulin production is increased by the pancreas. This results in an adjustment of insulin immunity.
This process is gradual. Excess energy is first stored in the fat cells for bad days. The problem with this is that the bad days never occur. Then the fat cells mutate into hormone glands that flood the body with pathogenic hormones.
This leads to an overload of the brain. It can also lead to leptin resistance. Leptin is responsible for the feeling of satiety.
Initially, the sugar metabolism disorder manifests itself through slightly increased/decreased urea, ferritin and blood count values.
These signs are followed by leptin resistance, diabetes 2, abdominal fat and metabolic syndrome up to neurodegeneration in the form of neuropathic pain and Alzheimer's disease.
In the book "Sugar - the secret killer", the connection between sugar consumption and various diseases is described in great detail.
How to overcome sugar addiction
From now on, you have to live exclusively on carrots. Of course, it doesn't work that way. To overcome sugar addiction, suffering, renunciation and relapse are not necessary.
Tip: Cook for yourself with real food and drink sugar-free.
A good way to overcome sugar addiction is to cook with real food and drink only sugar-free beverages.
Of course, the average 100 g of sugar is not consumed in the form of 47 sugar cubes. Most of the sugar we consume every day is in the products we buy in the supermarket.
Semi-finished and finished foods as well as industrially processed foods contain a lot of sugar. The latter often contain sugar as a flavour enhancer.
Especially in combination with fat and salt, our senses are deceived. We cannot tell whether the respective food is good or bad for us.
Food engineers are still searching for the ideal "bliss point", i.e., the optimal concentration of sugar, salt and fat. The interest of the taste buds is aroused by the sensory-specific saturation with flavour enhancers.
A portion of ready-made tomato soup contains 75% of the daily salt requirement and about 3.5 teaspoons of sugar. Would they really make this?
Around 20 to 30 grams of sugar are hidden in drinks. Whether it's a fruit juice, a glass of flavoured water or a soda, they all contain sugar. Even green cola counts about 22 grams per can.
Necessary to kick the sugar habit are the following things:
- Stabilisation of blood sugar levels
- Normalising the cortisol level
- Raising serotonin levels
Carbohydrates that slowly raise blood sugar levels are optimal. These include, in particular, foods with unbranched starch, fibre and a low glycaemic index. For breakfast, it is therefore better to eat spelt bread and a whole orange instead of orange juice, baguette or toast.
Most people's breakfasts are often sweet: Jam, muesli and nut-nougat cream are not to be missed. But when you look at the nutritional value table of ready-made muesli, you quickly notice that one portion contains about 15 to 25 grams of sugar.
Nutella is even more unhealthy. The popular nut-nougat cream consists of more than 50 % sugar. By using muesli mixes or nougat creams sweetened with natural sugar substitutes, it is not necessary to give up a sweet breakfast.
For example, there is already muesli with erythritol and Stevia, which not only tastes sweet in a balanced way, but also allows the blood sugar to rise to a small extent.
There is no need to have a guilty conscience when eating unprocessed, natural foods.
To make the sugar-free diet a success, it is important to make sure right from the start that you do not let more than 3 to 4 hours pass between meals. Otherwise, the brain panics and falls back into old stress patterns.
During the withdrawal from sugar addiction, a grain substitute can also be very helpful. Quinoa, for example, is a good choice. It is a very protein-rich so-called goosefoot plant. It looks similar to rice and can be used both savoury and sweet.
To have a good chance of success, you should give your body a time of 2 - 3 months to get used to the change. Everything should not be done "right" from the start.
The way out of sugar addiction works best if you take it in small steps. You should also be happy about every success, no matter how small, because this attitude causes the release of dopamine, which strengthens new neuronal connections in the brain.
The brain will demand the new positive habits again and again, because it learns quickly. Under acute stress, relapses in the form of food cravings are quite normal. However, they should not be a reason to give up.
Book recommendations on sugar addiction
Sugar - the secret killer

Get out of sugar addiction with the 4-step detox programme.
In the book "Sugar - the secret killer" this programme represents a part.
The concept is carried out for 12 weeks and is mainly based on the step-by-step withdrawal from starch and sugar.
- Taking stock: How much sugar do I eat? How do I feel before and after eating it? What are my personal sugar traps? Personal and, above all, feasible goals can be set with the copyable food diary.
- Getting to know nutritional components: There are detailed explanations of good and bad fats/carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins, which enable people to take more responsibility for their own nutrition.
- The authors also present other sugar alternatives. Especially in the initial phase, D (+) galactose is used first. This is a distillate in powder form, which is obtained from lactose and whey. D (+) galactose is metabolised independently of insulin. Later, Stevia and erythritol are also used.
- Implementation: This step is about applying the knowledge gained before in a practical way. What do I have to consider in the individual steps of the 3-month phase-out, which foods are optimal at which time?
- Activity: A light exercise programme can help immensely when quitting sugar addiction.
The book also provides scientifically sound information about the development of sugar addiction and its health consequences.
More than 60 sugar-free recipes in the chapter "In Sugar Heaven" conclude the book.
Goodbye sugar

Sugar-free happy in 8 weeks - With 108 recipes
The author of the book "Goodbye Sugar" suffered from a sugar addiction herself. For this reason, she decided to cut out sugar when cooking, baking, etc.
The first two weeks of the 2-month programme are uncomplicated and have the motto "I-just-play-with-this-idea". Here, simple steps like halving the sugar in your coffee are done first. Filled with lots of tricks, tips and sound knowledge, there is a precise plan each week.
With her book, Sarah Wilson proves that giving up sugar does not mean a reduction in quality of life.
With a collection of more than 100 delicious cooking suggestions, she also shows that you can also cook a wide range of dishes sugar-free.
The book also includes stock and shopping lists and illustrated pages throughout. It is highly recommended.

 German
German Dutch
Dutch French
French Italian
Italian Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish
