Blood glucose control | Blood glucose value
Interesting facts about blood glucose control for diabetics
The permanent control of the blood glucose level is an important component of the daily routine for diabetics. Find out here why you should pay the utmost attention to blood glucose control.
Good and healthy blood glucose control is the basis of diabetes therapy. Measurements at regular intervals help to prevent too high or too low values and to prevent secondary diseases.
Sugar in the blood is an essential substance for our body and its cells, because it obtains energy from glucose. The hormone of the pancreas, insulin, prepares the energy production by transporting the glucose dissolved in the blood into the cells.
There are different reasons why the blood sugar level rises in diabetics. In type 1 diabetes, no insulin is produced, as a result of which the sugar is not dissolved from the blood. This means that therapy consists of insulin injections.
Type 2 diabetics, on the other hand, produce enough insulin, but the cells do not react properly to it. This is why we speak of insulin resistance. Through frequent physical activity and reduction of excess weight, patients can lower their sugar levels and counteract their insulin resistance. If necessary, blood sugar-lowering tablets or insulin injections can be prescribed.
The success of the treatment depends greatly on the patient always monitoring his or her blood sugar level and adjusting the amount of tablets and insulin individually together with his or her doctor.
The risk of elevated blood glucose levels
A permanently elevated blood sugar level can have devastating consequences for the human organism. In most cases, however, symptoms appear only very late, and those affected initially feel neither pain nor other discomfort. If blood sugar levels are chronically elevated, nerves can be affected, arteries can calcify and the blood capillaries of the kidneys and eyes can be damaged. The following long-term damage can occur:
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Diabetic foot (foot ulcer with poor chances of recovery)
- Nephropathy (kidney damage)
- Damage to the retina

Diabetes finger and blood glucose measurement
Measuring blood glucose, but correctly!
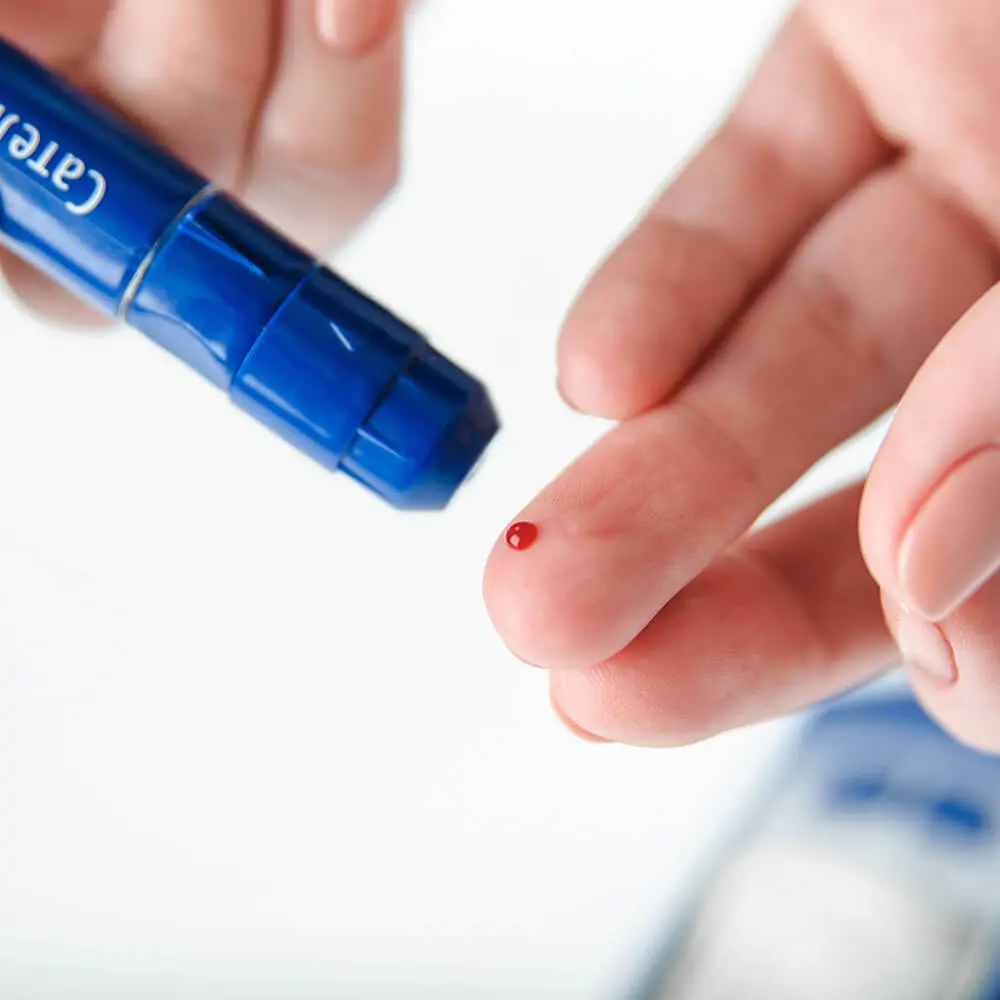
Measuring blood glucose on the finger
Regular checking of blood glucose is essential
A constant check of the blood sugar level is indispensable to avoid damage to the vessels, nerves and organs. Of particular importance here is the so-called HbA1c value, which is an indicator of the effectiveness of the therapy and the success of the blood sugar control.
It is a long-term value that shows the average blood sugar level of the last eight to ten weeks. Normally, the attending physician tries to keep the HbA1c value between 6.5 and 7.5 percent with an appropriate therapy. The blood glucose value is usually measured in an empty state, about two hours after eating.
Regular measurement of one's own blood glucose values is especially important in the adjustment phase, so that one knows whether the values are healthy, for example, after a meal or before sleeping, or what food, exercise or stress are doing.
With the help of these blood glucose values, many diabetics determine how much insulin needs to be injected with a meal or as a correction for too high blood glucose values. In addition, regular checks help to recognise tendencies towards very low or high values in good time, so that serious hypoglycaemia or hyperglycaemia can be avoided.
The blood glucose values measured at different times of the day are also relevant for the doctor, because he can use them to determine whether the diabetes setting is correct and base his decisions about therapy, such as new medication, on them.
Tips for measuring blood glucose
- Wash your hands thoroughly before measuring! Ideally with warm water, as this stimulates the blood circulation. If you do not have the opportunity to wash your hands, take the second drop of blood during the measurement.
- Massage the fingertip, as this also promotes blood circulation and simplifies the measurement.
- Prick the little, middle or ring finger and change fingers often. In everyday life, the thumb and index finger are used most often.
- Prick the side of the fingertip, because the blood collection is hardly painful there and many tiny blood vessels run there.
- The lancet must be changed before each blood collection. This is the only way to prevent infections and the pain is less with a fresh lancet because it is still very sharp.
- Last but not least: take care of your hands so that calluses do not form, which would make the pricking more painful.
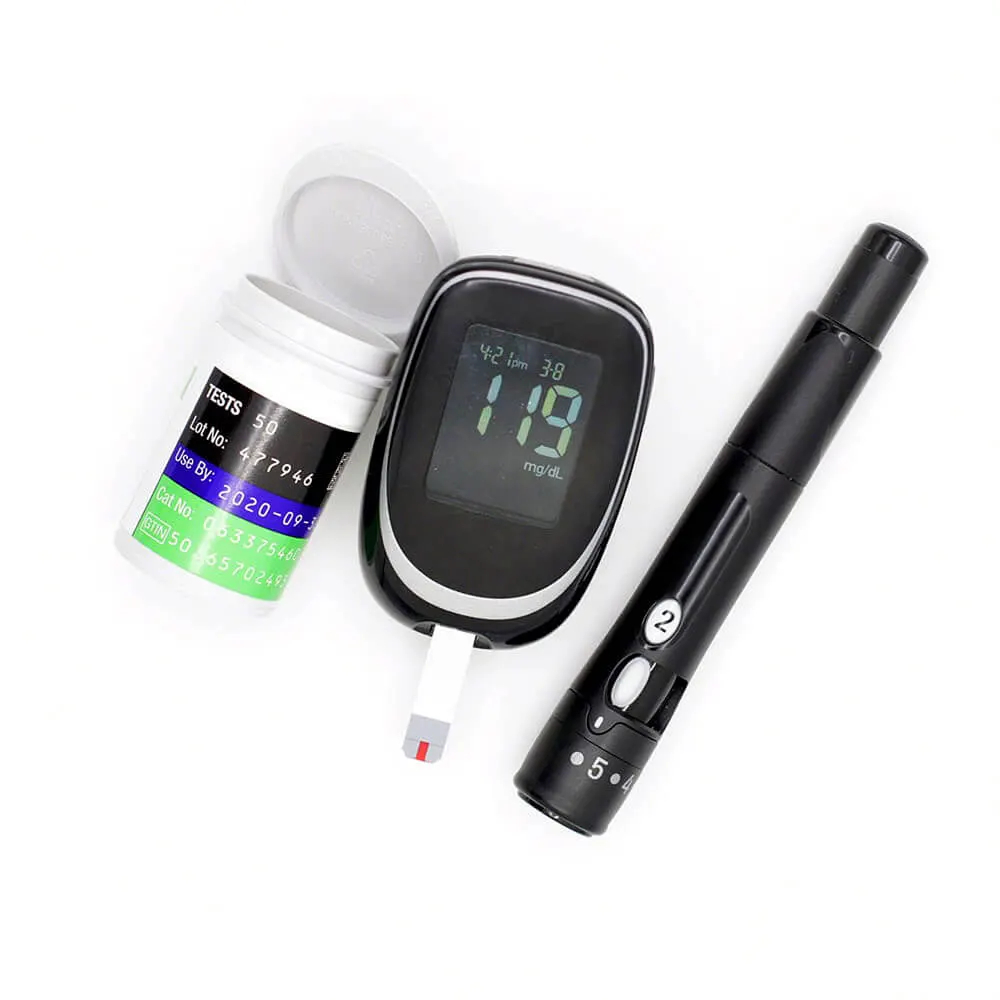
Diabetes test strips and blood glucose meter
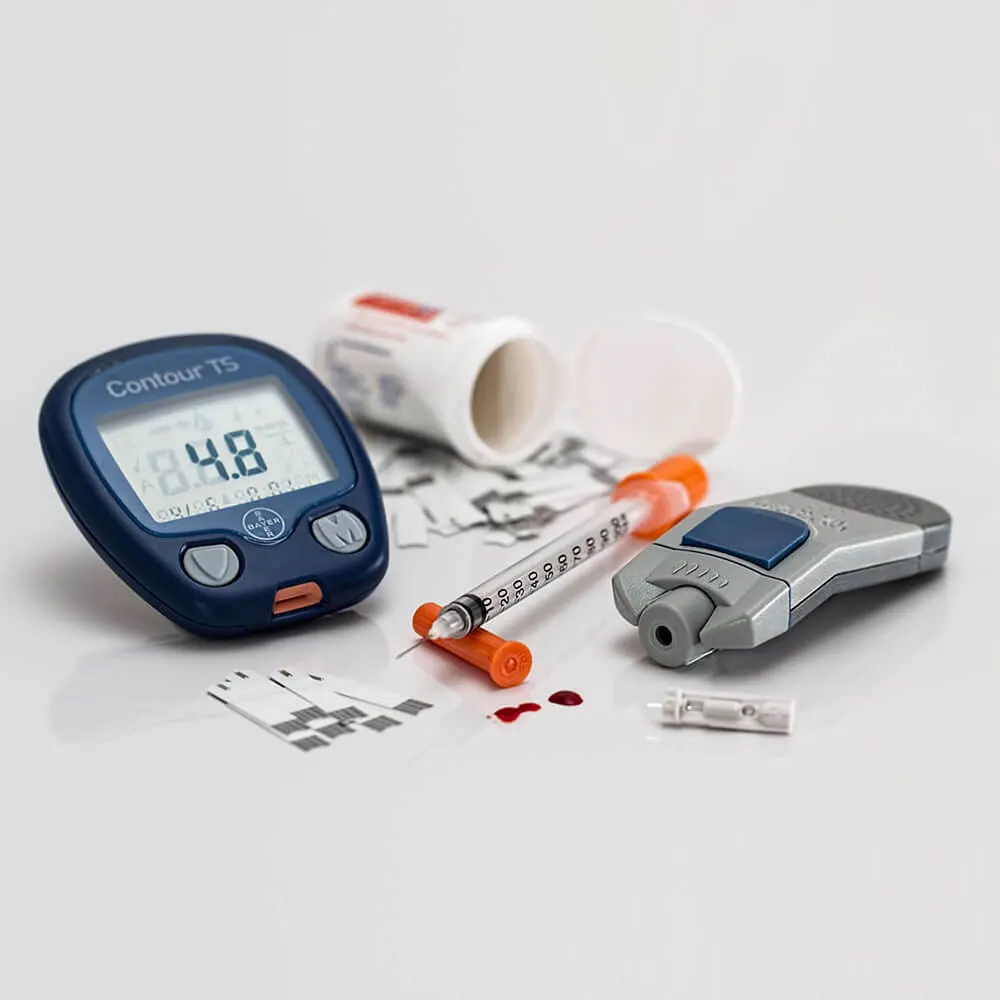
Blood glucose meter for determining the amount of glucose in the blood.
Accessories for blood glucose monitoring
To be able to identify possible fluctuations in blood glucose levels, it can be helpful to take several snapshots of the value. The more thorough and intensive the measurements are, the better the HbA1c value can be influenced.
To determine blood glucose levels, the amount of sugar in the blood serum is measured in milligrams per decilitre (mg/dl). In some cases, the percentage is also given in millimoles per litre (mmol/l). The normal range before eating is less than 100 mg/dl, about two hours after eating the blood sugar level should not exceed a value of 140 mg/dl.Important guideline values for blood glucose levels
In the meantime, regular monitoring of sugar levels has been greatly simplified by modern aids. When choosing a meter, patients with diabetes should pay special attention to the accuracy of the measurement and the ease of use. Taking blood samples with a lancet (extremely thin needle) is particularly painless. The lancing device is included in the set of most products.
Comparisons and field reports on various blood glucose meters can be found on various comparison portals. The criteria for comparing the devices include memory, accessories, dimensions and measuring range. Before buying, people should make sure that the meter meets their personal requirements.
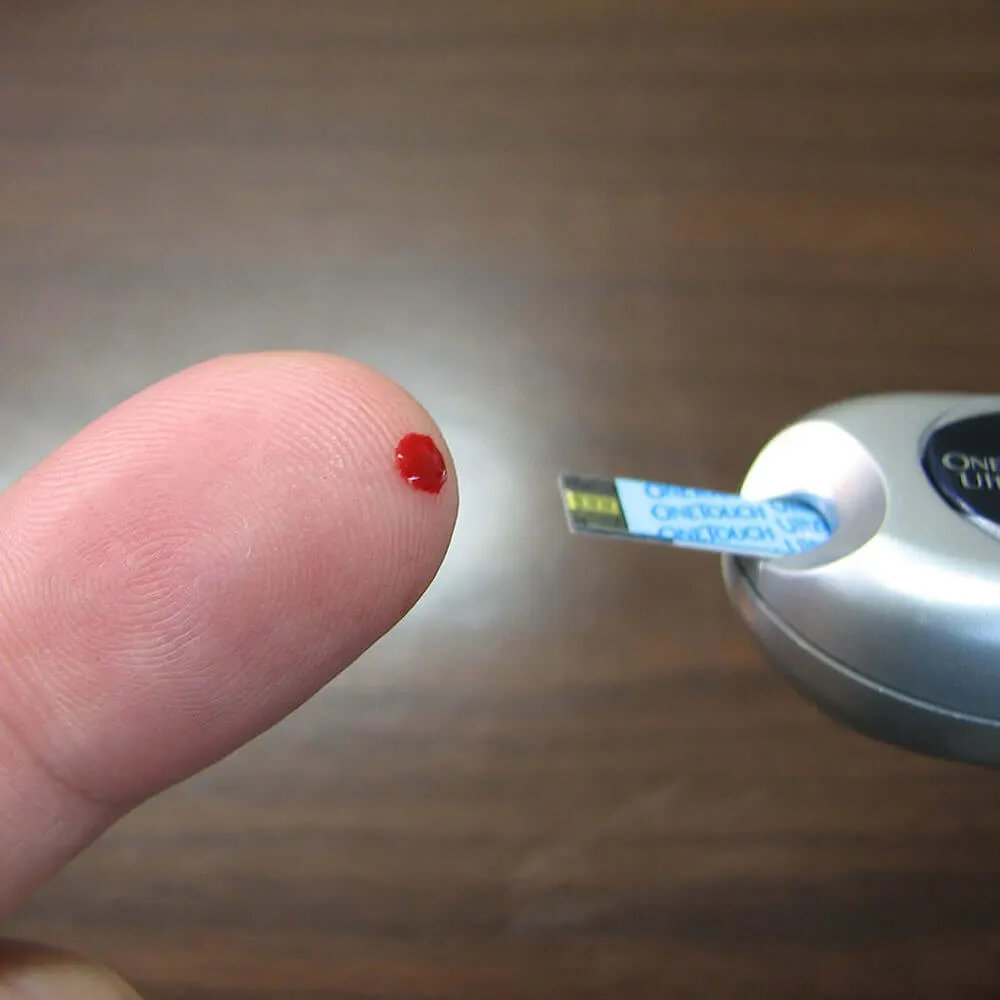
Blood glucose control to determine the glucose in the blood
Blood glucose control Diabetes and insulin injection
Ketoacidosis and hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar)
Hypoglycaemia occurs when the blood glucose level drops to less than 70 mg/dl. In some cases, hypoglycaemia can be fatal. Type 1 and 2 diabetics who are treated with insulin injections are particularly at risk.
Hypoglycaemia becomes particularly dangerous when symptoms are noticed too late or not at all. Under these circumstances, coma and unconsciousness can follow.
Ketoacidosis
In contrast to hypoglycaemia, blood sugar levels rise in a condition called ketoacidosis. Type 1 and type 2 diabetics in advanced stages are particularly at risk. An undetected ketoacidosis can lead to a complete loss of control of the metabolism. This can mean danger to the life of the person affected.
Checking blood glucose levels is also important during illness, because in most cases the insulin level rises sharply during various infections with fever. It makes sense to increase the hormone insulin, which has a short-term effect. A so-called ketone test can be carried out if there is a concrete suspicion.
The Diabetes Information Service has summarised which measures must be taken in case of hypoglycaemia or ketoacidosis and how to prevent the loss of control.
Intensity of blood glucose control
The required frequency of blood glucose monitoring depends on several factors and the therapy goal. The factors include, for example, individual fluctuations in blood glucose levels. The type of therapy is also decisive.
For diabetics who have to inject themselves with insulin, a higher intensity of control is necessary. Often, those affected check their blood glucose levels up to seven times a day. Normally, measurements are taken at least before going to bed, before driving and before each meal.
Measurements need to be taken much less often if the doctor has prescribed pre-determined amounts of insulin as injections or if the sugar level is particularly stable. Then a weekly profile of the blood glucose level is usually sufficient. To create this profile, several measurements of the blood glucose are taken on one day.
Some type 2 diabetics take blood sugar-lowering medication. In this case, blood glucose checks are often only necessary every few months.

In a nutshell:
In order to prevent extreme fluctuations in the blood glucose level, it is recommended in principle for every diabetic to check the blood glucose level regularly. Each measurement increases the chance of counteracting a possible loss of control at an early stage.
In addition, it is possible for those affected to develop a feeling for the changes in the value, for example during sport or meals, through regular measurements. So you could say: the more measurements you take, the easier it is to protect your own health in the best possible way and, above all, in the long term. So frequent checks are always worthwhile!

 German
German Dutch
Dutch French
French Italian
Italian Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish
